IMPACT OF CUPPING THERAPY AND PERCUSSIVE THERAPY IN FIBROMYALGIA PATIENT:A CASE REPORT
SALT Journal of Scientific Research in Healthcare
Volume 2, Issue 2, Page 11-15, Published on 06th October 2022
https://doi.org/10.56735/saltjsrh.ms2202021115
Case Report
HITAISHI TYAGI AND RITA SHARMA
Department of Physiotherapy, Sharda University, Greater Noida 201306, India
Corresponding Author: Dr. Rita Sharma, Assistant Professor, Department of Physiotherapy, SAHS, Sharda University, Greater Noida 201306, India.
ORCID ID: 0000-0002-3788-8977
Email: rita.sharma@sharda.ac.in
ABSTRACT
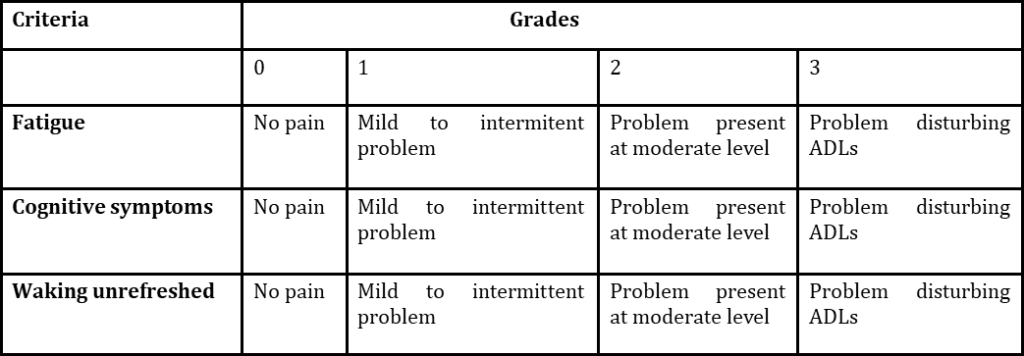
Fibromyalgia is a syndrome which has a clinical symptomatic feature of having pain in various regions of body part. Outcome measure were Visual analogue scale (vas) used for pain before and after the session. The present study highlight fibromyalgia and role of Physiotherapy in patients functional improvements. Cupping therapy and Percussive Therapy were given on trigger points. In a single session also both the treatment showed improvement in pain. Total duration of this study were six session in a week for two weeks. Cupping therapy and percussive therapy improves the overall quality of life of patient.
Keywords: Cupping Therapy, Fibromyalgia, Pain, Percussive Therapy, Theragun.
INTRODUCTION
Fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS) is chronic condition which causes pain and tenderness in the muscle , joint and tendon. FMS is generally present in middle aged females .The pain persist in different body party it usually covers the buttock region, neck, shoulder, chest and upper back . FMS is associated with anxiety and depression 1. FMS is associated with change in quality of life in worst conditions. The immunologic changes in FMS causes inflammation where neutrophils play an active role in inflammation 2.
On palpation the tender points in females are more than in males, although some researches have shown more that women experience more number of symptoms. The gender differences in this type of illness is generally not fully understood but depends upon sociocultural and biological factors 3.
The diagnostic criteria of FM is given by ACR (American College of Rheumatology)4
1. The Pain last for at least three months
2. The Tender points sites on palpation gives pain on both side of the body 1 :-
- a. Knee
- b. Low Cervical
- c. Trapezius
- d. Gluteal
- e. Greater Trochanter
- f. Second Rib
- g. Laterall Epicondlye
- h. Occiput
- i. Supraspinatus
A mechanical device, like the Theragun, is used for percussive massage in the percussive therapy approach, which has recently gained popularity. Percussive treatment is frequently used in practise to temporarily reduce discomfort and increase range of motion.
Cupping therapy is one of the effective ancient medical therapy practiced by ancient greeks, chinease and Egyptians. Cupping therapy relief muscular tension by increasing microcirculation and tissue detoxification. Cupping is one of the technique which enhance the quality of life of patients diagnosed with FMS 4.
Mechanism of cupping
The effects of sub-atmospheric pressure suction, boosting peripheral blood circulation, and enhancing immunity were the major hypothesised mechanisms of action. Cupping treatment has been reported to improve skin blood flow, change biomechanical aspects of the skin, increase pain thresholds, improve local anaerobic metabolism, reduce inflammation, and modulate the cellular immune system 5.
CLASSIFICATION OF CUPPING THERAPY
Cupping therapy is classified as follows 6.
Dry Cupping
Wet Cupping
Massage Cupping (Gliding/Dynamic)
Fire cupping
Ice cupping
Massage cupping is also known as dynamic cupping or gliding cupping in which the weak suction is made to move the cup or been glided over the skin surface by using oil or ultrasonic gel. This method is use in elderly people and young adults. The purpose of this study is to find out the effectiveness of cupping therapy and percussive therapy in fibromyalgia patient.
CASE REPORT
A 46-year-old female hostel warden who is right dominant experienced right shoulder pain since last 15 days. The patient first felt the same pain five years ago in the shoulder joint, which then spread to the scapular area. Although the patient’s right clavicle fractured in an accident 20 years prior and was successfully treated. The patient was motivated to exercise more as she used to perform bicep curls with a 4 kg weight on each side when her shoulder was not injured. But after 15 days, the pain starts to steadily intensify, occasionally becoming throbbing, stiff, and achy while engaging in shoulder abduction. Visual analogue scale( VAS)intensity rating was 7 out of 10. The patient complained of scapular and shoulder heaviness. The patient first visited an orthopaedic doctor and she was diagnosed fibromyalgia and prescribed 15 days of medication, after medication course only less than 10% of their symptoms had been relieved, and was then advised to visit Physiotherapist. Early in the morning, the shoulder became heavy and stiff, which makes it painful to handle anything heavy or difficulty in opening doors.
When compared to the opposite side, the patient appears to have normal skin tone, no redness, and no bruising where the discomfort is located. Patient makes use of all of their active ranges of motion, however pain only manifests during external rotation and abduction. The patient’s scapular region felt heavy and painful during flexion.
The patient reported pain in 4 distinct locations around the shoulder joint. On examination, there were 2 nodules over the upper trapezius muscles and 1 nodule over the superior border of the scapula. The supraspinatus muscle is located in the first region, followed by the medial scapular border, the belly of the biceps muscle, and the upper fibers of the trapezius muscle. While the patient was taking medicine, the pain in the biceps muscle belly stopped and instead began to arise over the triceps belly. MMT of elbow flexors and extensors was +4 grade, whereas MMT of shoulder flexors and abduction was +2 grade.
Patient claimed that her usual routines had changed, and she was unable to execute Activity of daily living(ADLs) like closing doors, preparing chapati, or lifting any weight without experiencing discomfort. As the patient was more inclined toward fitness, this has an impact on her quality of life.
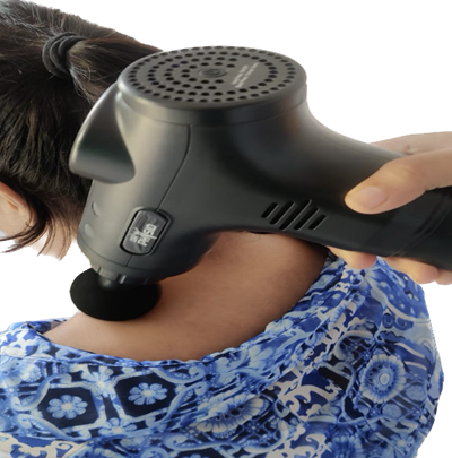
Fibromyalgia was identified in the patient. Percussive therapy technique given via theragun (fig-1) in which rhythmic continuous vibrations were given over the trigger point to stimulate the muscle and prevent muscle soreness.
Fig.1 Application of Theragun for releasing Trigger points

Cupping therapy was applied over the trigger points in which 5 min static and 5 min dynamic cupping were given to the patient (fig -2). After the single session of cupping and percussive therapy the patient experienced immediate alleviation in pain and reduction in muscle soreness and improvement in range of motion. Additionally, some isometric exercises and the usage of therabands, which use light and moderate resistance bands to strengthen the muscle are performed after the programme when the pain has totally subsided. Total Physiotherapy session was given to the patient was Six days once a week for two weeks and a total of 12 session were spent treating the patient with cupping therapy and percussive therapy by Physiotherapist.
Fig.2 Application of Cupping Therapy for releasing Trigger points

DISCUSSION
The average age of fibromyalgia patients is 45 years old, and the morbidity rises with age.
The five quality metrics in randomised clinical trials on cupping have improved since 10 years, according to certain clinical studies on this therapy. Patients’ quality of life has increased during the past 50 years as well 7.
The study in 2011 showed that interdisciplinary therapeutic approaches play an important role in the treatment of FMS. On discharge from hospital, the pain supporting the mental status of the patient has shown an improvement in symptoms 8. The case study intensively explored some theories which concerns about this therapy. It is justified that no theory could explained that how these multiple effects actually work under a single therapy. Since , various type of cupping therapy are responsible for circulatory changes as well as biochemical changes in the body. Theories explain major simple effects of cupping therapy with its types and their specificity . There are some biochemical properties changes of the skin and circulation due to reduction in pain. This is the only effectiveness of this therapy which make it different from other therapy. Measuring the diverse and multiple effects of cupping therapy is
limitation of this study. It is arduous to find out whether the result of cupping therapy is because of any of its type or step involved during the procedure. The details of each step in cupping mechanism are not known , making it difficult to have a scientific elucidation on how actually the mechanism work. This case study has put emphasis on the long lasting effect of cupping in the pain region. The two type of cupping is performed in this case study one is dry cupping and other is dynamic cupping which is been applied over the patient, giving 80% relief on daily basis .
Dynamic cupping is one of the type of massage cupping which requires dragging of cup with one to two suction over the pain region. It appears that previously mentioned mechanism of cupping therapy could not justifies all its consequences and for understanding the terminologies under this deeply , the further researchers are vindicate to develop more and more theories , RCTs and researches relevant to this customary technique. Moreover, the outcomes of researches suggest that the idiosyncratic of this technique holds patient’s satisfaction indeed8,9. One of the main limitations of this study was the short duration of the study which was of 2 weeks and no follow up was done.
CONCLUSION
In this study cupping therapy and percussive therapy technique improves the overall quality of life of the patient. After 12 session,6 days in a week for 2 weeks patient showed marked improvement in pain, range of motion and muscle soreness.
REFERENCES
- Jahan F, Nanji K, Qidwai W, Qasim R. Fibromyalgia syndrome: an overview of pathophysiology, diagnosis and management. Oman Med J. 2012 May;27(3):192-5. https://doi.org/10.5001/omj.2012.44. PMID: 22811766; PMCID: PMC3394355.
- Aslaner H, Çalış HT, Karabaşc Ç, Benli AR. Hemogram parameters in fibromyalgia and effects of wet cupping therapy on hemogram parameters. World Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine. 2022 Oct 1;8(4):497. https://doi.org/10.4103/wjtcm.wjtcm_73_21
- Yunus MB. Gender differences in fibromyalgia and other related syndromes. J Gend Specif Med. 2002 Mar-Apr;5(2):42-7. PMID: 11974674.
- Lauche R, Spitzer J, Schwahn B, Ostermann T, Bernardy K, Cramer H, Dobos G, Langhorst J. Efficacy of cupping therapy in patients with the fibromyalgia syndrome-a randomised placebo controlled trial. Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 17;6:37316. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep37316. PMID: 27853272; PMCID: PMC5112514.
- Sharma R. Therapeutic effects of cupping therapy in frozen shoulder: a review article. SALT J Sci Res Healthc. 2021 Nov 02; 1(2): 35- 37. https://doi.org/10.56735/saltjsrh.ms2101023537
- Cao HJ, Liu JP, Hu H, Wang NS. Using a partially randomized patient preference study design to evaluate the therapeutic effect of acupuncture and cupping therapy for fibromyalgia: study protocol for a partially randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2014 Jul 10;15:280. https://doi.org/10.1186/1745-6215-15-280. PMID: 25012121; PMCID: PMC4226966.
- Cao H, Han M, Li X, Dong S, Shang Y, Wang Q, Xu S, Liu J. Clinical research evidence of cupping therapy in China: a systematic literature review. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2010 Nov 16;10:70. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6882-10-70. PMID: 21078197; PMCID: PMC3000376.
- Romeyke T, Scheuer HC, Stummer H. Fibromyalgia with severe forms of progression in a multidisciplinary therapy setting with emphasis on hyperthermia therapy-a prospective controlled study. Clin Interv Aging. 2014 Dec 19;10:69-79. https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S74949. PMID: 25565789; PMCID: PMC4279606.
- Al-Bedah AMN, Elsubai IS, Qureshi NA, Aboushanab TS, Ali GIM, El-Olemy AT, Khalil AAH, Khalil MKM, Alqaed MS. The medical perspective of cupping therapy: Effects and mechanisms of action. J Tradit Complement Med. 2018 Apr 30;9(2):90-97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcme.2018.03.003. PMID: 30963043; PMCID: PMC6435947.
ARTICLE TYPE: Case Report;
ORCID ID: Open Researcher and Contributor Identifier (ORCID) ID of corresponding author: https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3788-8977;
ETHICAL: Institutional ethical committee and prior patient consent obtained;
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: None;
FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE: The authors declare that there was no financial aid received.;
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: No conflict of interest associated with this research work.;
AUTHORS CONTRIBUTION: H.T., and R.S., reviewed and wrote the article for publication.;
AUTHORS AFFILIATIONS: Ms. Hitaishi Tyagi, BPT Intern Student, Department of Physiotherapy, SAHS, Sharda University, Greater Noida 201306; Dr. Rita Sharma, Assistant Professor, Department of Physiotherapy, SAHS, Sharda University, Greater Noida 201306, India.;
CORRESPONDING AUTHOR EMAIL: rita.sharma@sharda.ac.in ;
ARTICLE CITATION: Tyagi H & Sharma R. Impact of cupping therapy and percussive therapy in fibromyalgia patients: a case report. SALT J Sci Res Healthc. 2022 October 06; 2(2): 11-15.
PUBLISHER’S NOTE: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.




© Hitaishi Tyagi & Rita Sharma.
Originally published in the SALT Journal of Scientific Research in Healthcare (https://saltjsrh.in/), 06.10.2022.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work, first published in the SALT Journal of Scientific Research in Healthcare (https://saltjsrh.in/), is properly cited. The complete bibliographic information, a link to the original publication on https://saltjsrh.in/, as well as this copyright and license information must be included.
